MEL II: Two elemental resources
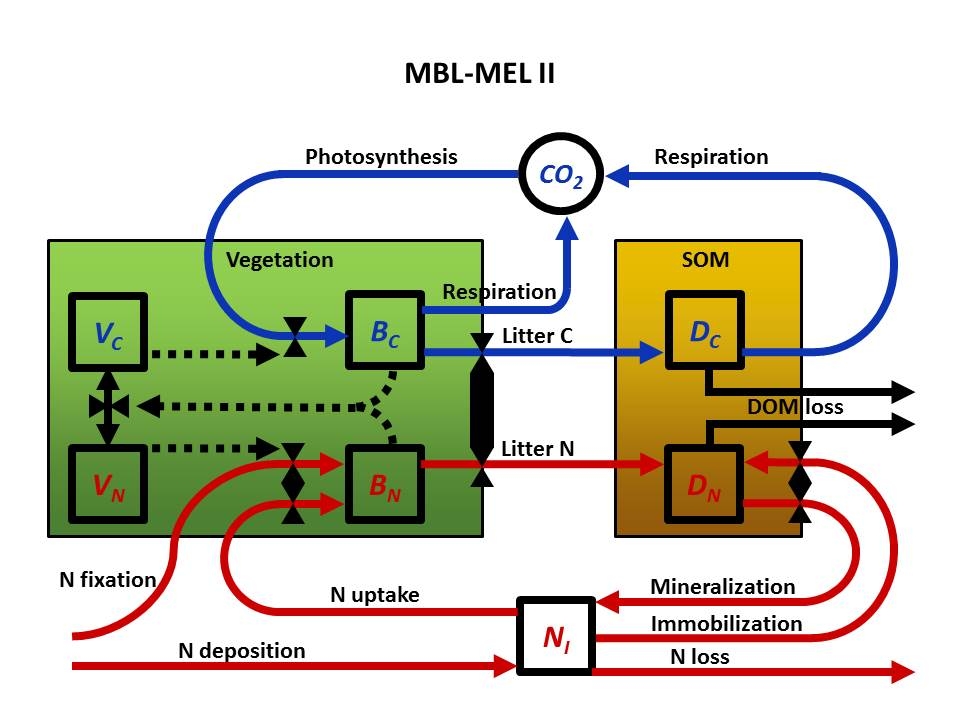
In MBL MEL II (Fig. 1), carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) are cycled among available inorganic pools (CO2,╠řNi), biomass in vegetation (BC,╠řBN), and soil detritus (DC,╠řDN). A microbial community is implied in the model structure, but its biomass is not explicitly represented. Microbial biomass is assumed to be part of soil detritus.
Inorganic N is depleted through losses from the ecosystem (N loss, e.g., leaching or gas fluxes), uptake by microbes (Immobilization), and uptake by vegetation (N Uptake). Inorganic N is replenished from sources outside the ecosystem (N Deposition) and by mineralization of soil organic matter (Mineralization). Elements are taken up by vegetation at a rate that is a Michaelis-Menten function of element concentration (Ni) and is proportional to the surface area of vegetation that is active in uptake of that element (Si). We have examined several alternate formulations of the uptake equation (Rastetter and Shaver 1992), and currently use one in which╠řSi╠řis a fractional power function of vegetation biomass. As biomass increases, there is a diminishing uptake return with increasing╠řSi╠ř. However, this formulation does not capture late-successional decreases in leaf area observed in some forests.
Vegetation biomass is assumed to be roughly proportional to the amounts of the two elements in the vegetation. However, because the model allows transient deviations of the element ratio from a nutritionally balanced state, it would be inappropriate to calculate biomass based solely on one element or the other. Therefore, we calculate vegetation biomass based on the abundance of both elements (BC╠ř+╠řqBN, where╠řq╠řis the optimum C:N ratio) and, for convenience, express it in C units.
The heart of the MEL model is the algorithm for reallocating plant assets expended toward resource acquisition (biomass, proteins, carbohydrate...). We refer to these assets as the uptake effort and lump them into a single abstract variable. We assume that the total uptake effort is limited, but increases with the vegetation biomass. The fraction of the total effort that is allocated toward the uptake of resource╠ři╠řis represented by the variable╠řVi╠ř(no units), which can change through time as the availability of, or requirement for, resource╠ři╠řchanges. Because╠řVi╠řis the fraction of the total uptake effort, the sum of the two╠řVi╠řmust be 1, which implies that
dVCdt+dVNdt=0
(i.e., increases in one╠řV╠řmust be compensated by a decrease in the other╠řV). All else being constant, acquisition of resource╠ři╠řincreases monotonically (but not necessarily linearly) with increasing╠řVi╠řand uptake of resource╠ři╠řis zero when╠řVi╠řis zero.
Projects
ÔÇóSpecies, community and ecosystem level consequences of the interactions among multiple resources (DEB-0108960), June 2001 ÔÇô May 2005.