Full Name
Andrew Gillis
Title
Associate Scientist

- Email:
- Phone:
- Fax:
- CV:
File
- ORCID ID:
0000-0003-2062-3777
M.Sc. Palaeobiology, University of Bristol, 2005
B.Sc. (Hons), Biology, Dalhousie University, 2004
The Gillis lab is an interdisciplinary team of embryologists, physiologists, engineers and palaeontologists, with a shared aspiration to understand the development and evolution of the vertebrate body plan. We work extensively with embryos of cartilaginous fishes (sharks, skates and holocephalans), though our work is very comparative, and incorporates a wide range of emerging and established developmental model systems. Current projects in the Gillis lab include:
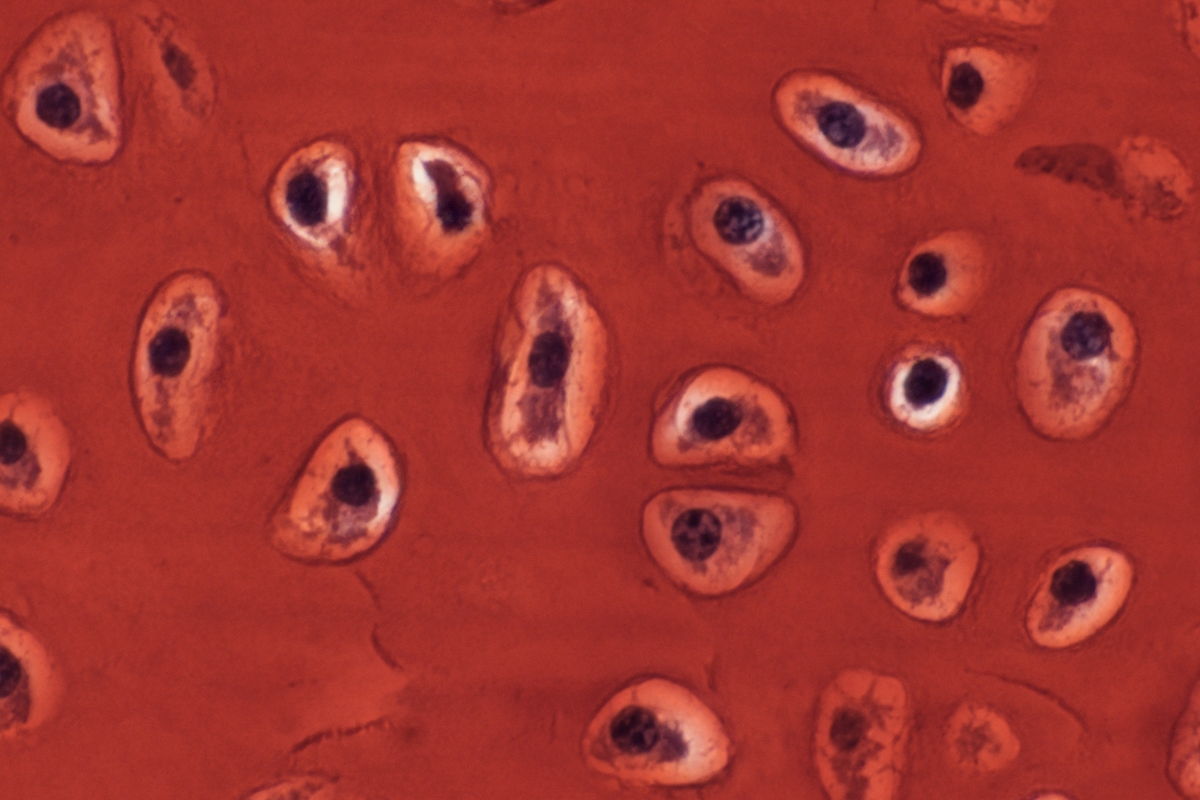
Development, growth and repair of cartilage: In mammals, cartilage is predominantly an embryonic tissue. Most mammalian cartilage is replaced by bone, with cartilage persisting permanently at only a few sites within the adult skeleton (e.g., in joints, as articular cartilage). Mammalian articular cartilage has a very poor capacity for spontaneous repair, hence the prevalence of debilitating joint diseases like osteoarthritis. Unlike mammals, cartilaginous fishes have a skeleton that is composed entirely of cartilage, and that remains cartilaginous throughout life. Moreover, we recently discovered that skates possess a unique progenitor cell type that continues to make new cartilage through adulthood, and that facilitates the spontaneous repair of cartilage injuries. We are investigating the molecular basis of adult cartilage growth and repair in the skate, with an eye to developing novel therapeutic strategies for mammalian articular cartilage disease.
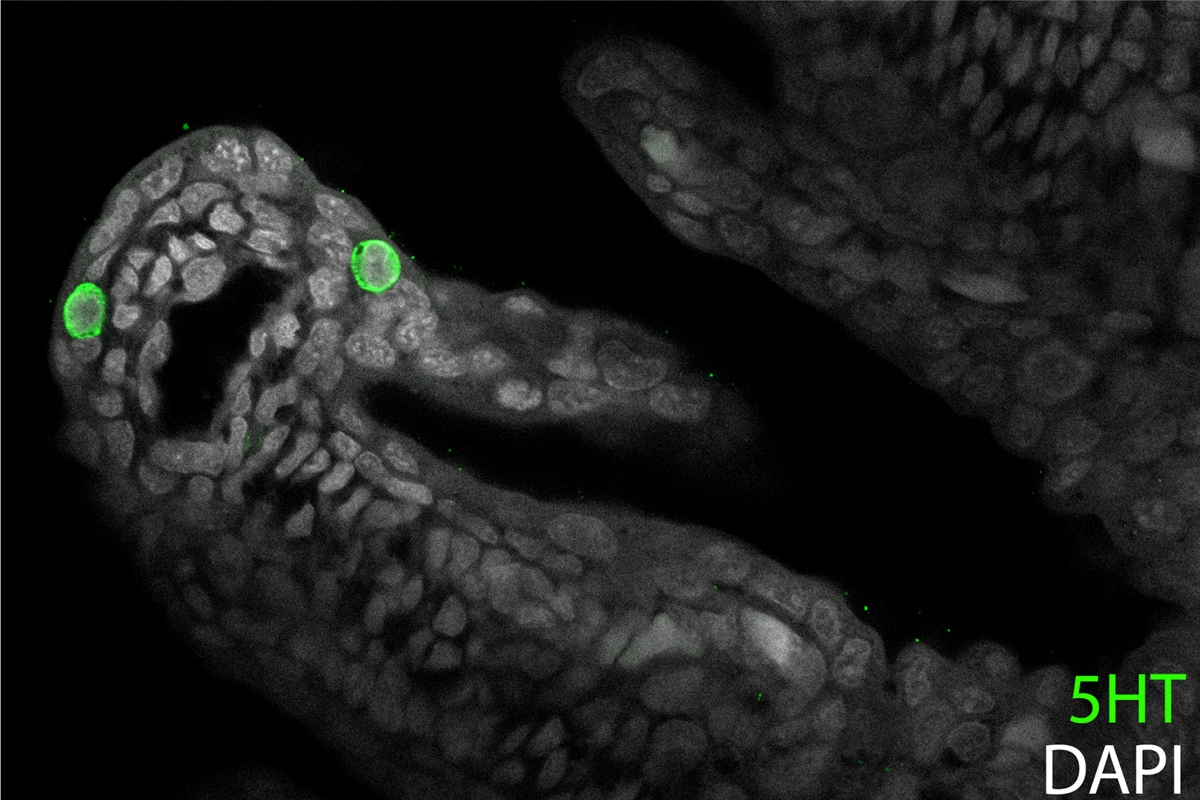
Diversity and evolution of neuroendocrine cell types: Neuroendocrine cells (NECs) are a diffuse and poorly understood assemblage of cell types that have collectively been called the “third branch” of the vertebrate nervous system. These cells play an integral role in mediating an organism's physiology and behaviour by releasing neuropeptides in response to changing environmental conditions or stress. In humans, the aberrant growth or function of NECs forms the basis of several aggressive cancers. We are systematically investigating the diversity, embryonic origin and homology of NEC types across a range of vertebrate and non-vertebrate taxa, and testing whether/how the origin of new NEC types is associated with major transitions in animal evolution.
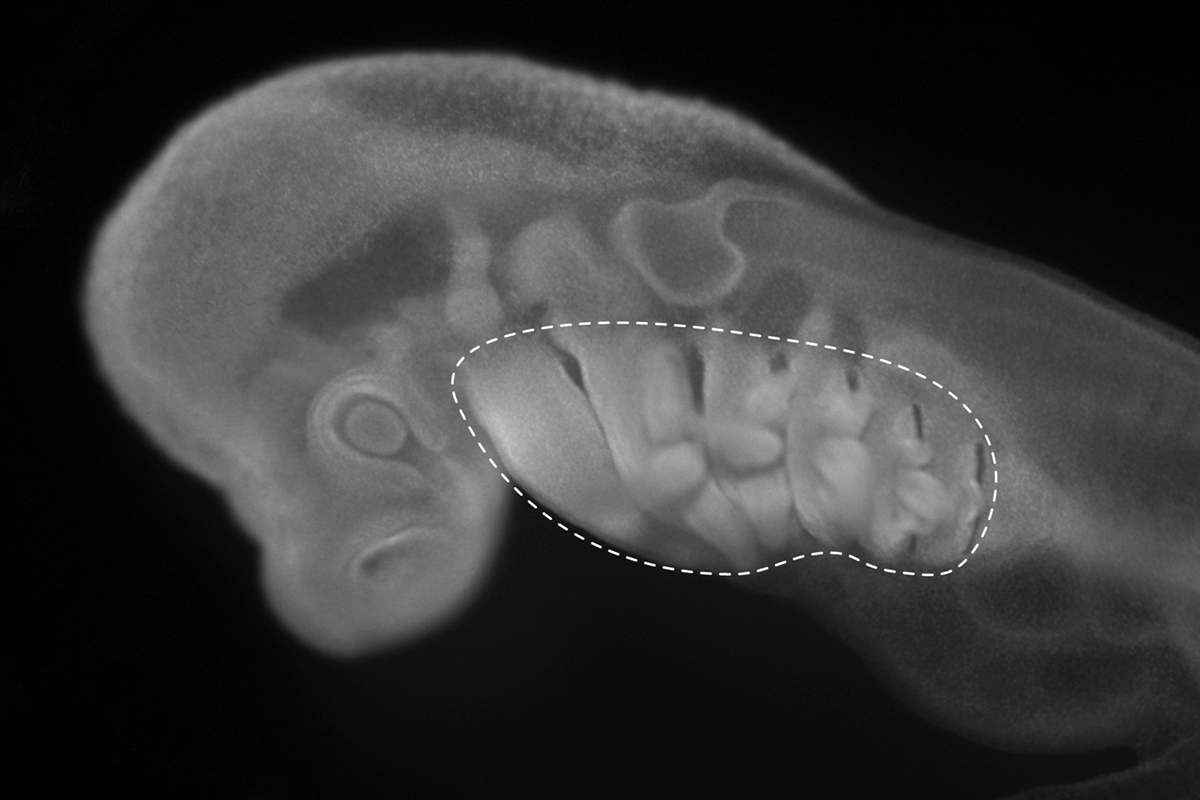
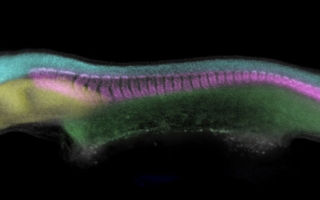
Development and evolution of vertebrate pharyngeal arches: Pharyngeal arches are paired columns of tissue that arise on either side of the embryonic vertebrate head. Pharyngeal arches give rise to much of the craniofacial skeleton – including the jaw and gill skeleton of fishes and the jaw, laryngeal and middle ear skeleton of tetrapods – and mispatterning of pharyngeal arches accounts for many vertebrate congenital craniofacial anomalies. We are investigating the molecular mechanisms that pattern pharyngeal arches in a range of vertebrate and non-vertebrate taxa, in order to understand how these structures arose in evolution, how pharyngeal arch tissue interactions occur robustly during development to ensure proper patterning of the craniofacial complex, and how pharyngeal arch patterning mechanisms have evolved to give rise to anatomical diversity and novelties, such as jaws, gills and paired fins.


Criswell KE, Roberts LE, Koo ET, Head JJ, Gillis JA (2021) Proc. Nat’l Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118: e2114563118.
Hirschberger C, Sleight VA, Criswell KE, Clark SJ, Gillis JA (2021) Molecular Biology and Evolution 38: 4187-4204.
Sleight VA, Gillis JA (2020) eLife 9: e60635.
Marconi A, Hancock-Ronemus A, Gillis JA (2020) eLife 9: e53414.
Criswell KE, Gillis JA (2020) eLife 9: e51696
Gillis JA, Alsema EC, Criswell KE (2017) Proc. Nat’l Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114: 13200-13205.
Gillis JA, Tidswell ORA (2017) Curr. Biol. 27: 729-732.
Gillis JA, Hall BK (2016) Development 143: 1313-1317.